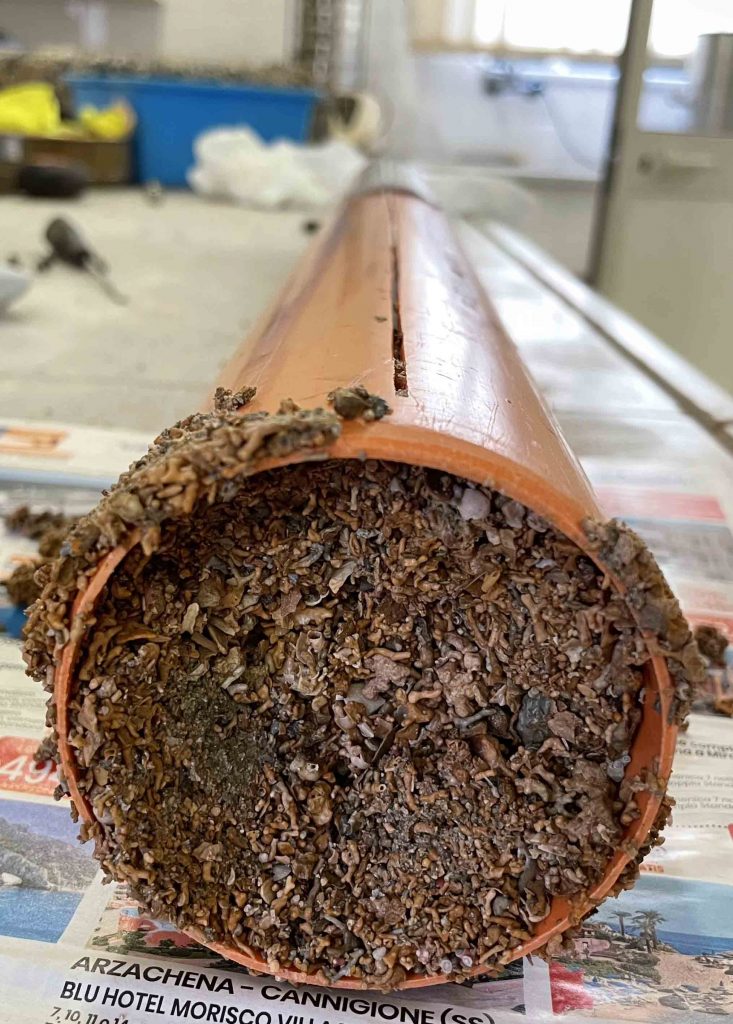
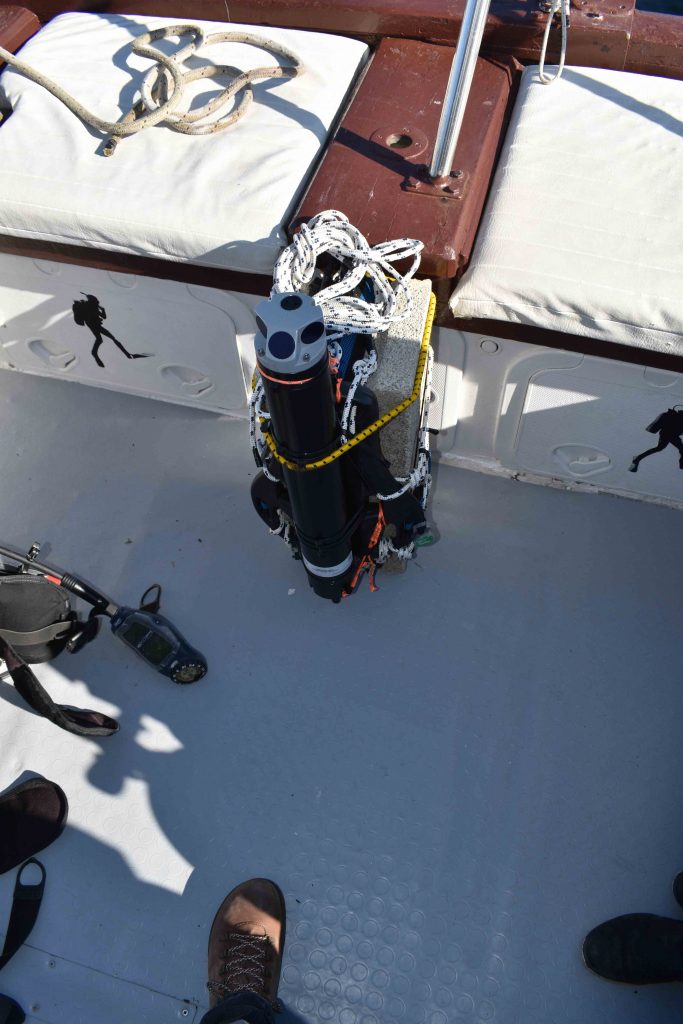
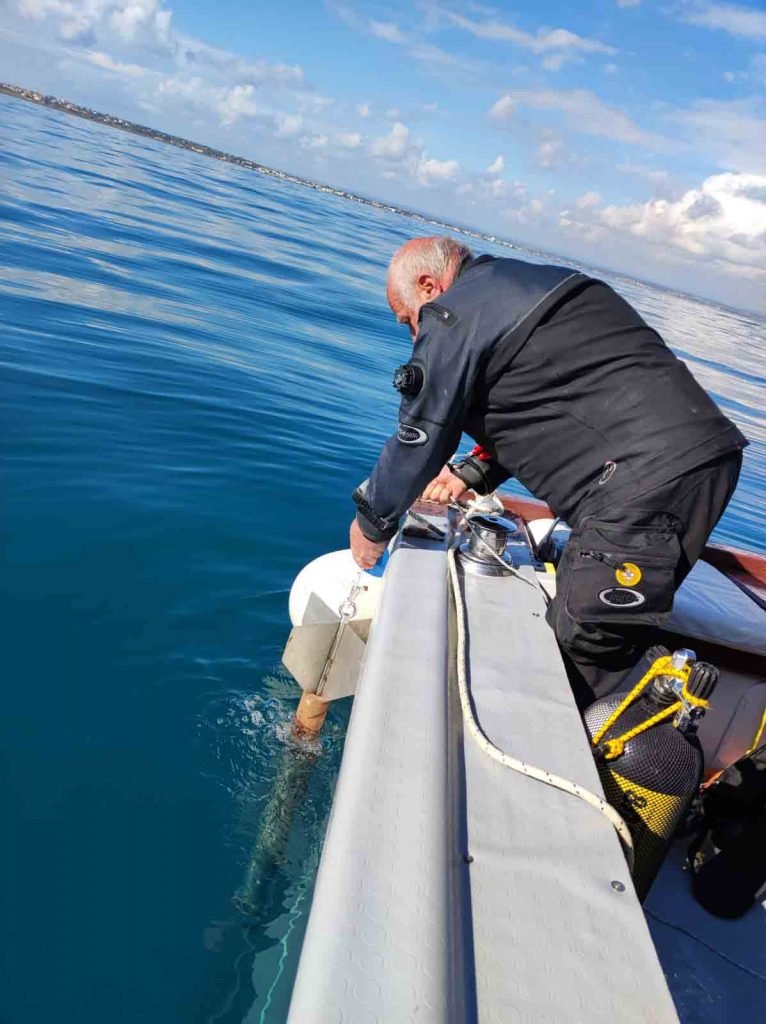
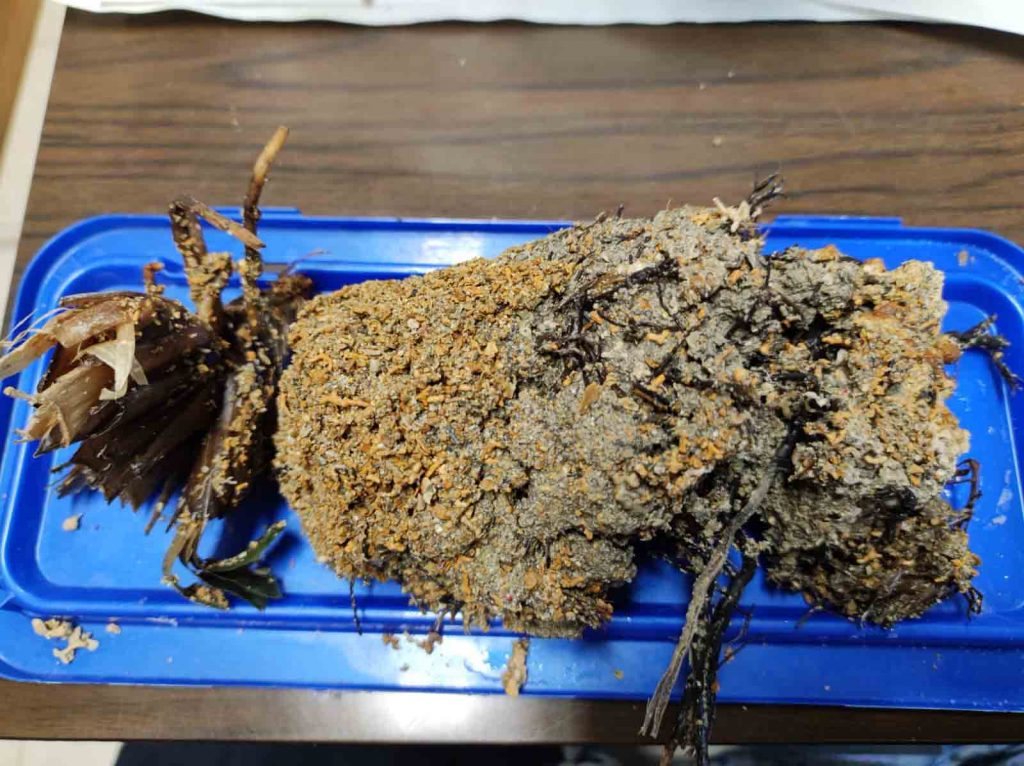
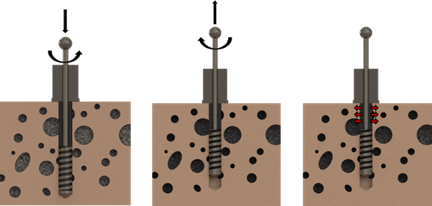
During the coring operation, high stability is required due to the brittleness of the coralligenous samples. In order to reach this stability, the ROV has to be firmly anchored to the reef surface. Hence, we designed an ad hoc anchoring system by testing different types of screw: the common ones used for wood, self-drilling screws, and finally drill bits commonly used for concrete and metals. The first two options failed because an excessive axial force was needed and the resulting thread was not able to withstand enough pulling force. Instead, the last option seemed to be the best since it allows easier penetration in the material. Then, a specifically designed test rig was used to find the current consumption and the axial thrust required to penetrate in the coralligenous sample.



However, drill bits alone are not sufficient to assure vertical force resistance so we are going to mate them with a rubber expansion sleeve. Once the holes are made, a mechanism is going to move up just the tip of the screws that is opportunely constrained to it by a sphere on the top. Hence, each rubber sleeve is going to be compressed and will expand providing sufficient grip with the sidewalls of the holes.
Specific tests already validated such a system but we cannot wait to try it underwater!